How to Fix a Slow Website: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide
Fix a Slow Website is critical for any business, blog, or online store because speed directly affects user experience, search visibility, and revenue. A slow website frustrates visitors, increases bounce rates, and lowers trust. Research proves that when a site takes more than three seconds to load, most users abandon it before engaging with the content. Even a one-second delay can reduce conversions by up to seven percent, which, for businesses, can translate into thousands of dollars in lost sales each month. For e-commerce websites, this could mean fewer completed checkouts, while for service providers, it could result in missed leads and inquiries. Beyond user frustration, search engines like Google also reward fast websites with better rankings because speed is considered a core web vital. This means that even if your content is high-quality, a competitor with a faster site could outrank you and capture your traffic. In a digital world where attention spans are short and alternatives are plenty, speed becomes a deciding factor between gaining or losing a customer.
Slow websites not only reduce immediate sales but also hurt long-term growth, as users are less likely to return to a site that offers a poor experience. The good news is that website performance issues can be fixed with proper optimization. By addressing factors such as heavy images, unoptimized code, weak hosting, and lack of caching, businesses can achieve dramatic improvements in load times. Faster websites create a smoother browsing experience, boost search engine rankings, and increase conversion rates, ultimately leading to higher revenue and stronger online presence. This guide will cover each important step in detail so you can identify what slows your website down and learn how to optimize it effectively.
Test the Speed of Your Website
The first step in fixing a slow website is always to test its current performance. Without testing, it is impossible to know whether your website loads in three seconds or ten seconds, and it is equally difficult to measure improvements after optimization. There are many free and reliable tools available online that provide detailed speed reports. Google PageSpeed Insights is one of the most popular tools because it gives both mobile and desktop performance scores along with actionable recommendations.
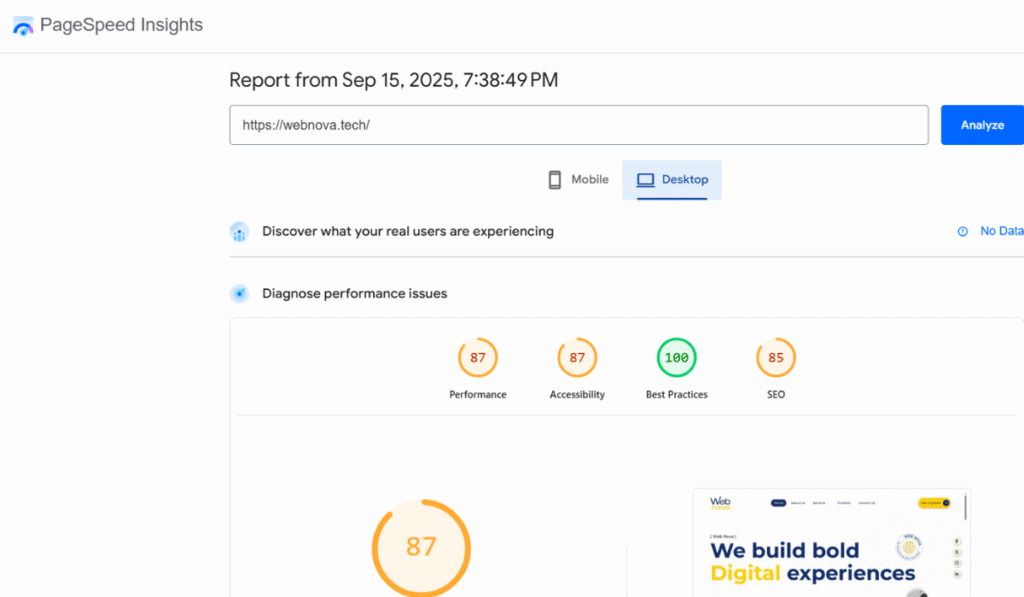
GTmetrix is another excellent choice as it shows loading time, total page size, and requests made by the browser. Similarly, Pingdom Website Speed Test offers an easy-to-understand summary of performance issues. When you test your site, pay attention to three main metrics: First Contentful Paint (FCP), which measures how fast the first piece of content appears; Time to Interactive (TTI), which shows how soon the site becomes usable; and overall page load time. These results will serve as a benchmark to compare improvements once you apply optimization techniques.
Optimize All Images on Your Website
Images are often the largest files on a website and can significantly slow down loading speed if not optimized properly. Many website owners upload high-resolution images directly from cameras or stock photo websites without resizing or compressing them, which results in unnecessarily large file sizes. To fix this, always resize images to match the display requirements of your website. For example, if your blog page only displays images at 800 pixels wide, uploading a 3000-pixel-wide photo makes no sense and only slows down loading. Additionally, the format of the image plays a critical role. For photographs, JPEG is usually the best option because it offers a smaller size with decent quality.
For graphics, logos, or icons with transparency, PNG is more suitable. However, modern formats like WebP are highly recommended because they provide excellent quality at a much smaller size and are supported by most browsers. Compression tools such as TinyPNG, Squoosh, or online WordPress plugins can automatically reduce image size without noticeable quality loss. On Shopify or other e-commerce platforms, third-party apps and built-in optimization features also help ensure faster image delivery. By optimizing images, you can often reduce page size by more than fifty percent, which leads to instant speed improvements.
Enable Browser Caching for Faster Reloads
Caching is another essential method for improving website speed. When a user visits your site for the first time, their browser downloads files such as images, CSS, and JavaScript. If caching is enabled, the browser stores these files locally so that when the user visits again, the browser loads them from the local cache instead of requesting them from the server again. This significantly reduces loading time on repeat visits. On WordPress, caching can easily be managed using plugins like WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache, or LiteSpeed Cache.
Which not only enable browser caching but also provide advanced features like database optimization and preloading. Shopify users do not have manual caching options since the platform manages it automatically, but they can still benefit from other optimizations. For websites running on custom servers, caching can be enabled through the server configuration files such as .htaccess on Apache or nginx.conf on NGINX. When properly configured, caching ensures that returning visitors experience lightning-fast page loads, improving both user satisfaction and engagement.
Minify and Combine CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Every website is built using code, and while code is necessary, excessive or unoptimized code can slow down performance. Many websites contain extra spaces, line breaks, comments, or unused CSS and JavaScript files that increase page size without adding value. Minification is the process of removing unnecessary characters from code, which reduces file size and speeds up loading. Combining multiple CSS and JavaScript files into single files can also reduce the number of HTTP requests made by the browser, which directly improves speed.
For WordPress, plugins like Autoptimize or Asset CleanUp make this process simple by automatically minifying and combining files. Developers can also use build tools such as Webpack or Gulp to automate minification during development. In addition to minification, it is equally important to remove render-blocking resources that delay page rendering. By carefully managing CSS and JavaScript, websites become lighter and more responsive, which results in better user experience and improved Google PageSpeed scores.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Another major factor affecting website speed is the geographical distance between the user and the web server. If your website is hosted on a server in the United States but your visitor is accessing it from Asia, the data must travel a long distance, which causes delays. A Content Delivery Network (CDN) solves this problem by distributing your website’s content across multiple servers located around the world. When a user visits your site, the CDN automatically serves content from the nearest server, reducing latency and improving speed. Cloudflare is one of the most popular free CDNs, offering features like caching, DDoS protection, and SSL support. Paid CDNs such as Akamai, StackPath, or KeyCDN offer advanced optimization features for businesses with global audiences. Integrating a CDN is relatively simple, and once activated, it ensures faster delivery of images, CSS, JavaScript, and other static resources to users worldwide.
Improve Your Web Hosting Performance
Even after applying all optimizations, your website may remain slow if your hosting server is weak or overloaded. Shared hosting plans are affordable but often suffer from slow performance because resources are shared among multiple websites. If your site attracts high traffic or runs heavy applications, upgrading to better hosting is essential. Cloud hosting solutions such as SiteGround, Hostinger, Bluehost, or AWS provide scalable resources that adjust according to demand, ensuring consistent performance.

Virtual Private Servers (VPS) or dedicated servers also offer powerful performance for larger websites. The choice of hosting depends on your budget, but investing in high-quality hosting is often the most effective solution for long-term speed improvement. Remember, hosting is the foundation of your website, and without strong hosting, other optimizations may have limited impact.
Remove Unnecessary Plugins and External Scripts
Many websites, especially those built on WordPress, become slow because of too many installed plugins. While plugins add functionality, each plugin also loads additional scripts, styles, and database queries, which increase load time. To solve this problem, review your plugins regularly and deactivate those you don’t use. Also, replace heavy plugins with lighter alternatives whenever possible. For example, instead of using a bulky page builder plugin, consider using a lightweight theme with built-in customization options. Apart from plugins, external scripts like ad trackers, chat widgets, or third-party integrations can also slow down performance. Only keep scripts that are absolutely necessary for your business, and remove the rest. By reducing the number of plugins and external scripts, you will notice significant improvements in website loading speed.
Enable Lazy Loading for Media Files
Lazy loading is a smart technique that improves speed by delaying the loading of images and videos until they are needed. Normally, when a web page loads, the browser downloads all images, even those that appear below the fold and may not be seen immediately. Lazy loading ensures that only the images visible on the screen load first, while others load when the user scrolls down. This reduces initial page load time and saves bandwidth. On WordPress, lazy loading can be enabled using plugins like a3 Lazy Load or by enabling built-in lazy load features in modern versions. Shopify and many modern CMS platforms already support lazy loading. Implementing lazy loading is especially useful for image-heavy websites like blogs, news portals, and e-commerce stores.
Monitor, Re-Test, and Maintain Speed Regularly
Optimizing website speed is not a one-time task. Once you have applied all the above techniques, you need to re-test your site using the same tools mentioned earlier. Compare the results with your initial benchmarks to see how much improvement has been achieved. Sometimes, one optimization may fix the problem, but in other cases, multiple layers of optimization are required. Monitoring speed should be part of regular website maintenance because new content, plugins, or design updates may introduce fresh issues. Setting up performance monitoring tools such as Google Analytics Site Speed reports or New Relic ensures that you are notified whenever performance drops. Continuous monitoring guarantees that your site remains fast, reliable, and optimized for both users and search engines.
Conclusion
Website speed is no longer just a technical concern; it is a critical factor that influences user experience, search rankings, and business success. A slow website frustrates visitors, reduces engagement, lowers conversions, and damages brand reputation. By following the strategies explained in this guide—testing speed, optimizing images, enabling caching, minifying code, using a CDN, improving hosting, reducing plugins, enabling lazy loading, and monitoring performance—you can transform a sluggish website into a fast, responsive platform that keeps visitors engaged and happy. Fast-loading websites not only attract more traffic but also convert better, which directly impacts revenue and growth. If you want to stay competitive in the digital marketplace, optimizing website speed should always remain a top priority.
